If you weren’t able to join Thursday’s webinar, SL Advisors Midstream Energy and Inflation Outlook, you can watch a recording here.
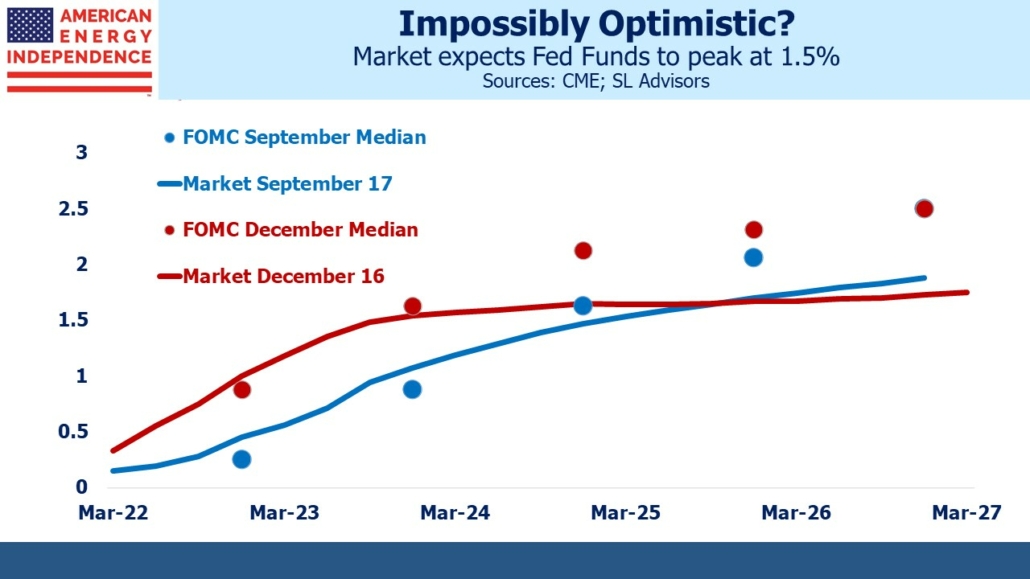
The media referred to the Fed’s “hawkish pivot” following Wednesday’s revised dot plot and faster taper. More accurate is that chair Jay Powell confirmed that the FOMC was following the market’s earlier revisions to the rate outlook. Eurodollar futures traders and the Fed are once more synchronized over the next couple of years in looking for the Fed Funds rate to reach around 1.5%. Forecasts diverge beyond that, with fixed income traders comfortable that rates will peak, whereas FOMC members expect continued increases. When it comes to forecasting even their own actions, history shows the Fed has much to be humble about.
The great penalty of inflation is suffered by fixed income investors, who conventionally demand a return at least as high to preserve purchasing power. Negative real yields on G7 sovereign debt are muting the market’s concern about value erosion. Persistently low bond yields that result are supporting risk assets such as equities. Buoyant bond and stock markets mean that there has been very little pressure on the Fed to act. The pleas for tighter policy have not come from financial markets, but from well-qualified observers such as former Treasury secretary Larry Summers and former NY Fed leader Bill Dudley. A handful of politicians have expressed concern about inflation, but Congressional enthusiasm for tighter policy will expire before the first rate hike.
The result is that financial markets regard today’s high inflation as relatively costless. Return-oriented investors in US government debt should demand high real rates as compensation for the dire fiscal outlook. But return-insensitive buyers (central banks; pension funds) dominate, and their acceptance of guaranteed value erosion is a subsidy that makes inflation more tolerable.
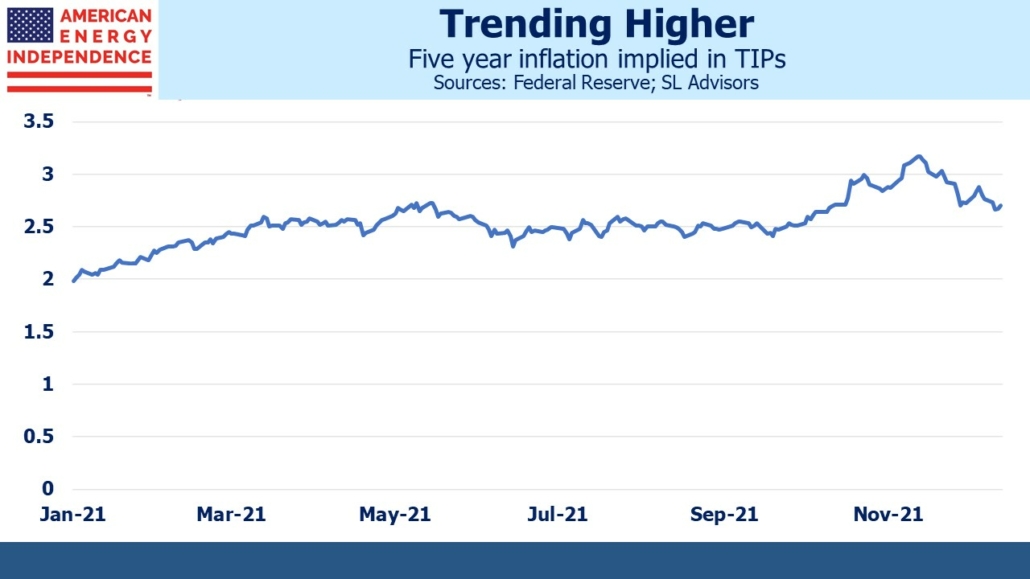
Five year inflation expectations derived from TIPs yields began the year at 2%, and reached 3.1% a month ago although have moderated recently. The Fed targets Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) Inflation whereas TIPs settle against CPI. Technical differences mean PCE inflation runs lower than CPI – about 0.5% since 2000 but 0.3% since 2008. The bond market’s long term inflation outlook is a little higher than the FOMC’s long term 2% forecast even adjusting for PCE/CPI differences.
The consensus interpretation of the yield curve is that raising short term rates to 1.5% will be sufficient to bring inflation back to the Fed’s 2% target. An alternative explanation is that financial markets, and therefore the Fed, will tolerate higher inflation.
The Fed and most analysts expect declining inflation next year. Criticism flows easily when inflation is rising, but if it moderates as expected next year the FOMC will draw a collective sigh of relief. They’ll still taper and normalize rates, but the pressure from opinion leaders will be off. If Owners’ Equivalent Rent (OER), the quixotic survey-based measure of the cost of shelter, increases expect the Fed to look past it as a non-cash expense.
The absence of financial market stress during the current inflationary spurt will lessen the urgency to follow the rate path they’ve laid out. A hint of economic weakness will embolden those wishing to pause normalization. The flat yield curve would steepen.
Spiraling Federal debt and fortuitously low (negative) real rates make moderately higher inflation in America’s interests. The resilience of financial markets affords the Fed flexibility in normalizing rates and tolerance for a slower return to 2% inflation – or indeed inflation settling at a somewhat higher level.
The “hawkish pivot” shouldn’t be confused with a hawkish Fed. They simply followed the market. Their tolerance for temporarily higher inflation in support of full employment, the revised interpretation of their mandate announced last year, represents a more dovish approach to monetary policy. It’s one they’ve been following faithfully ever since.
Midstream energy infrastructure, as we noted in Thursday’s webinar, still offers attractive yields with decent upside through real assets that should provide protection against inflation.
We have three funds that seek to profit from this environment:
Energy Mutual Fund
Energy ETF
Inflation Fund
Please see important Legal Disclosures.
The post Inflation’s Upside Risk appeared first on SL-Advisors.