A Potemkin economy has lured the Fed, economists, and Wall Street analysts into a potentially dangerous assumption of economic normalcy. However, with a review of how we got here, we can better understand the costs and consequences of monetary interventions.
“In 1783, after the Russian annexation of Crimea from the Ottoman Empire and the liquidation of the Cossack Zaporozhian Sich, GrigoryPotemkin became governor of the region. Crimea, devastated by the war, and the Muslim Tatar inhabitants became viewed as a potential fifth column of the Ottoman Empire. Potemkin’s major tasks were to pacify and rebuild the country by bringing in Russian settlers.
In 1787, as a new war was about to break out between Russia and the Ottoman Empire, Catherine II, with her court and several ambassadors, made an unprecedented six-month trip to New Russia. One purpose of this trip was to impress Russia’s allies prior to the war. Another purpose was to familiarize herself, supposedly directly, with her new possessions. To help accomplish this, Potemkin set up “mobile villages” on the banks of the Dnieper River. As soon as the barge carrying the Empress and ambassadors arrived, Potemkin’s men, dressed as peasants, would populate the village. Once the barge left, the village was disassembled, then rebuilt downstream overnight.” – Wikipedia
While there is some debate about the accuracy of the story, in politics and economics, a Potemkin village is any construction (literal or figurative) whose sole purpose is to provide an external façade to lead the population to believe the country is faring better than reality.
A reasonable amount of data suggests the Federal Reserve and the Government created such a facade.
A Potemkin Market
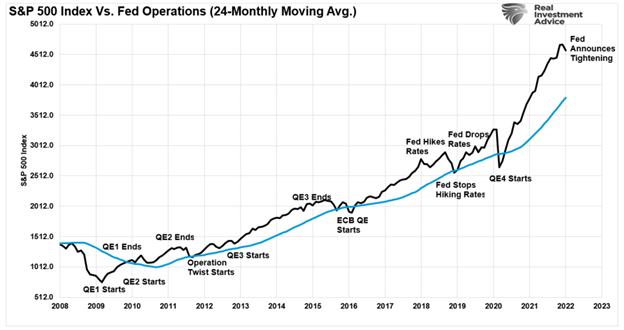
In 2008, the global economy shook from a “credit crisis” unlike anything witnessed since the “Great Depression.” As a result, the Federal Reserve, international central banks, and governments coordinated to inject massive amounts of monetary and fiscal policy into the financial and economic system. It seemed to have worked as financial markets recovered and the banking system survived.
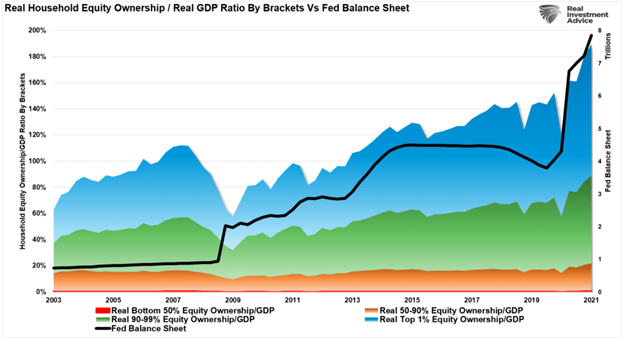
The problem, much like our story, the financial interventions created a facade of prosperity. The rich, who had assets to invest, benefitted greatly. But, unfortunately, the bottom 50% of the economy got no benefit at all.
Of course, as shown in the chart above, each time the Federal Reserve removed its accommodations, the facade of financial success quickly faded. Such then required new interventions to create the illusion of growth.
After more than a decade, it should not be surprising we see attacks on capitalism and demands for socialism. Notably, there has been an increase by the bottom 90% of income earners the #SystemIsBroken, to steal a hashtag.
But it isn’t just the financial markets.
A Potemkin Economy
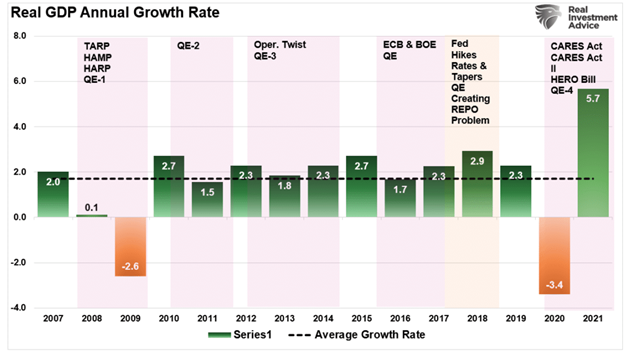
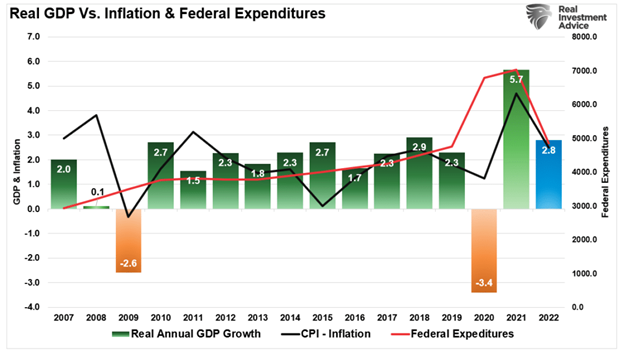
In 2021, the economy grew at the fastest annual rate since the early 1980s. At 5.7% annualized growth, it is not surprising that economists and analysts are suggesting the economy is in full recovery. However, as shown below, much like the financial markets, it is more akin to a Potemkin economy, given the massive fiscal and monetary programs needed to support it.
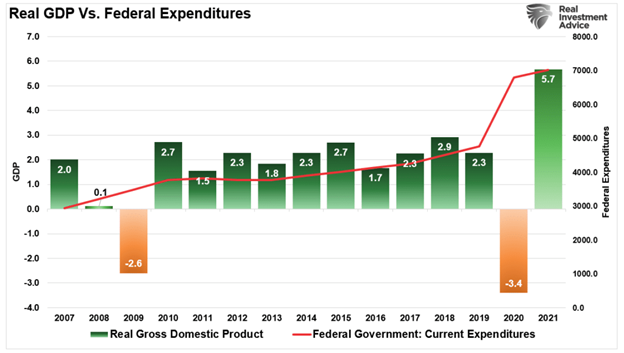
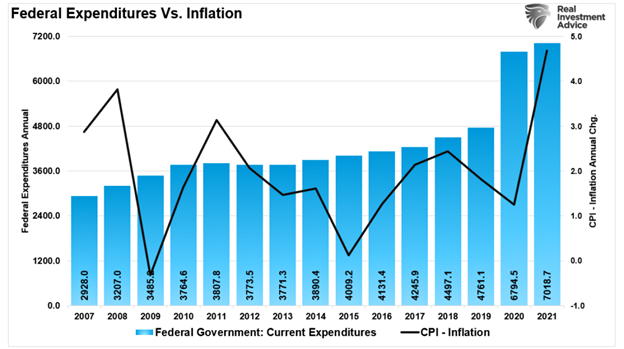
Such is more apparent if we overlay annualized economic growth rates with Federal expenditures. Not surprisingly, the increase in expenditures from $4.5 trillion to more than $7 trillion led to a surge in economic growth.
Furthermore, given that surge in fiscal policy was targeted directly at households, it is not surprising that inflation surged with it.
The Fed is now discussing reversing monetary policy (by hiking interest rates and reducing their balance sheet) to quell inflation. However, beginning in 2022, the fiscal impulse will decline sharply, removing the facade of economic strength. As a result, inflation will decrease as economic growth contracts.
Not surprisingly, given that the current spike in inflation, and economic growth, was a function of massive liquidity infusions, the reversal will be deflationary. Such will put the Fed in the very precarious position of making a policy mistake.
The Failure Of The Facade
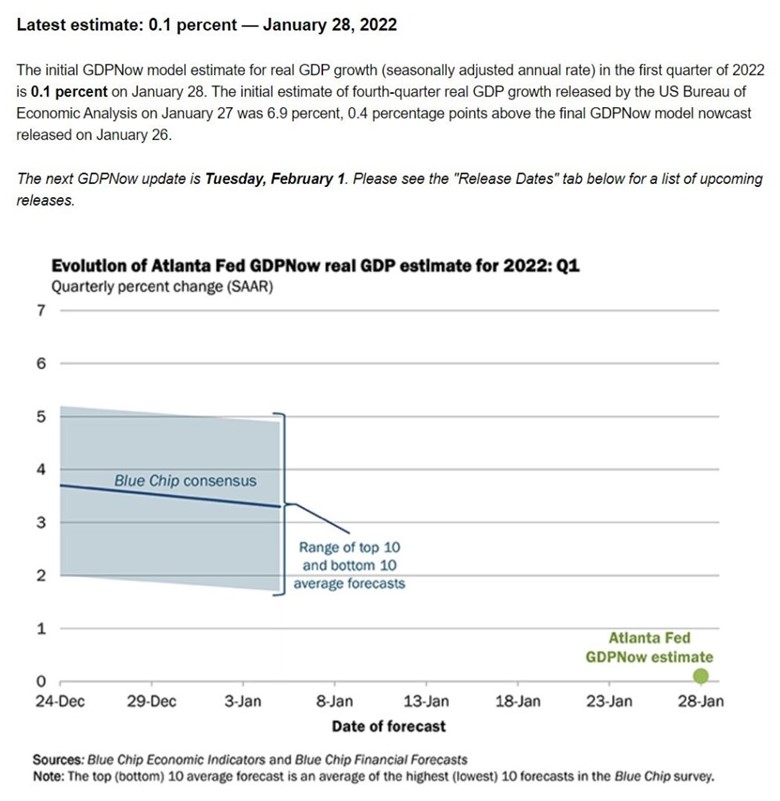
While mainstream media and economists don’t fully understand the narrative of a Potemkin economy, evidence of its failure is growing. At the end of January, the Atlanta Federal Reserve released its initial estimate of the first-quarter GDP growth rate. At just 0.1%, such suggests the economy is slowing rapidly without support from additional fiscal and monetary policy.
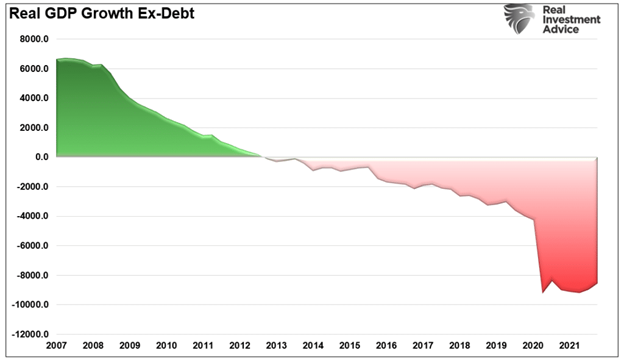
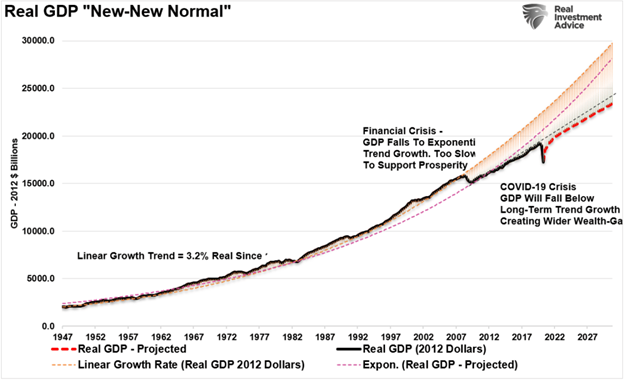
As noted above, after decades of increasing debt levels in the economy, which diverts capital from productive growth to debt service, the rise of the “wealth inequality” should be of no surprise. As shown, without increasing debt levels, there would be no economic growth at all. Much like Potemkin’s village, while the economy may have “appeared” to grow, economic growth was “negative” without debt increases. The chart below shows what economic growth would be without increasing federal debt.
The deterioration of economic growth is seen more clearly in the chart below.
From 1947 to 2008, the U.S. economy had real, inflation-adjusted economic growth with a linear growth trend of 3.2%.
However, following the 2008 recession, as debt surged, the growth rate dropped to the exponential growth trend of roughly 2.2%. Unfortunately, the Federal Reserve provided policies that fostered even greater unproductive debt and leverage levels instead of reducing outstanding debt problems.
Pulling Forward Consumption Isn’t Sustainable.
Following the 2020 recession, the economic growth trend will remain below the previous growth trend. Such is simply a function of the massive amounts of debt added to the overall system, retarding future economic growth.
The “trap” lawmakers and the Fed are in is “stimulus’ only pulls forward future consumption. But, as we saw after the initial CARES act, as soon as financial support evaporated, so did economic growth.
The hope over the last decade was the economy would eventually “catch fire” and grow organically. Such would allow Central Banks to reverse monetary supports. However, such never occurred as Central Banks reduced monetary support, the economy stalls, or worse.
It is clear something has gone wrong for the Federal Reserve. The ability to pull forward future consumption through monetary interventions is less effective each time. Despite ongoing hopes of higher growth rates in the future, such continues to not come to fruition as the “economic divide” worsens.
While the U.S. economy exited the recession in 2021, it may well be a “Potemkin” economic result rather than a recovery leading to broader prosperity.
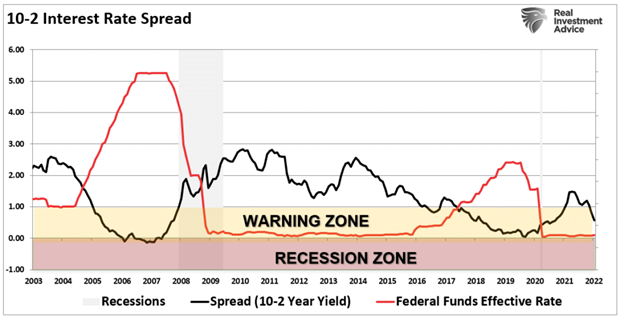
The most significant risk is the Fed becoming aggressive with tightening monetary policy to the point something breaks. That concern will manifest itself as a disinflationary impulse that pushes the economy towards a recession. The yield curve may be telling us this already.
Due to the debt, demographics, and monetary and fiscal policy failures, the long-term economic growth rate will run well below long-term trends. Such will only widen the wealth gap, increase welfare dependency, and push demands for socialism, slowly killing the “golden goose” of capitalism.